When to Use CSR-Based Issuance
CSR-based certificate issuance is recommended when:- You need to maintain control of your private key
- Your security policy requires keys to be generated on the target system
- You’re integrating with Hardware Security Modules (HSMs)
- You want to use a specific key that already exists
- You’re working with systems that generate their own CSRs (e.g., load balancers, network appliances)
Generating a CSR
Prior to requesting a certificate, a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) must be generated. While multiple tools and workflows are available, the example below illustrates how to generate a CSR using OpenSSL.Generate a New Key and CSR
Generate CSR from Existing Key
Generate CSR with Subject Alternative Names
Generate CSR with ECDSA Key
Verify Your CSR
Before submitting, verify your CSR contents:CSR Format Requirements
Your CSR must meet the following requirements:- Format: PEM-encoded PKCS#10 Certificate Signing Request
- Required header:
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE REQUEST----- - Required footer:
-----END CERTIFICATE REQUEST-----
Supported Key Algorithms
| Algorithm | Supported Sizes/Curves |
|---|---|
| RSA | 2048, 3072, 4096 bits |
| ECDSA | P-256, P-384, P-521 |
Supported Signature Algorithms
| Key Type | Supported Hash Algorithms |
|---|---|
| RSA | SHA-256, SHA-384, SHA-512 |
| ECDSA | SHA-256, SHA-384, SHA-512 |
Guide
Configure a Certificate Authority
Before you can issue any certificate, you must first configure a Certificate Authority (CA).The CA you configure will be used to issue the certificate back to your client; it can be either Internal or External:
- Internal CA: If you’re building your own PKI and wish to issue certificates for internal use, you should follow the guide here to create at minimum a root CA and an intermediate/issuing CA within Infisical.
- External CA: If you have existing PKI infrastructure or wish to connect to a public CA (e.g. Let’s Encrypt, DigiCert, etc.) to issue TLS certificates, you should follow the documentation here to configure an External CA.
Note that if you’re looking to issue self-signed certificates, you can skip this step and proceed to Step 3.
Create a certificate policy
Next, follow the guide here to create a certificate policy.The certificate policy will constrain what attributes may or may not be allowed in the request to issue a certificate.
For example, you can specify that the requested common name must adhere to a specific format like
*.acme.com and
that the maximum TTL cannot exceed 1 year.If you’re looking to issue TLS server certificates, you should select the TLS Server Certificate option under the Policy Preset dropdown.Create a certificate profile
Next, follow the guide here to create a certificate profile
that will be referenced when requesting a certificate.The certificate profile specifies which certificate policy and issuing CA should be used to validate an incoming certificate request and issue a certificate.
You should specify the certificate policy from Step 2, the issuing CA from Step 1, and the API option in the Enrollment Method dropdown when creating the certificate profile.
CSR-based issuance requires a Certificate Authority. Self-signed certificates are not supported when using a CSR.
Issue a certificate with your CSR
- Infisical UI
- API
To issue a certificate using your CSR, navigate to your Project > Certificates > Certificate Requests and click Request.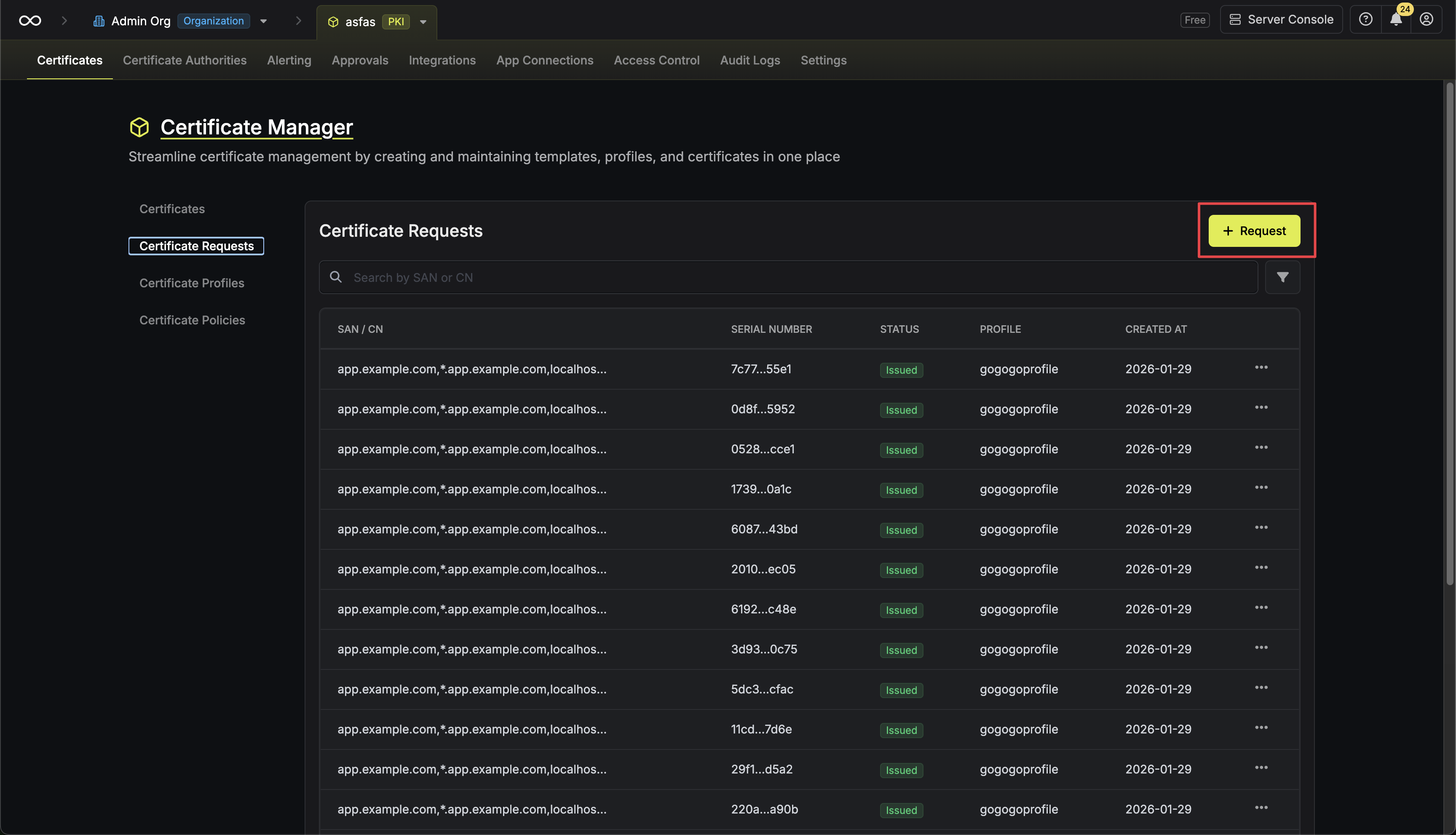 Select CSR (Certificate Signing Request) as the Request Method, then choose your certificate profile.
Select CSR (Certificate Signing Request) as the Request Method, then choose your certificate profile.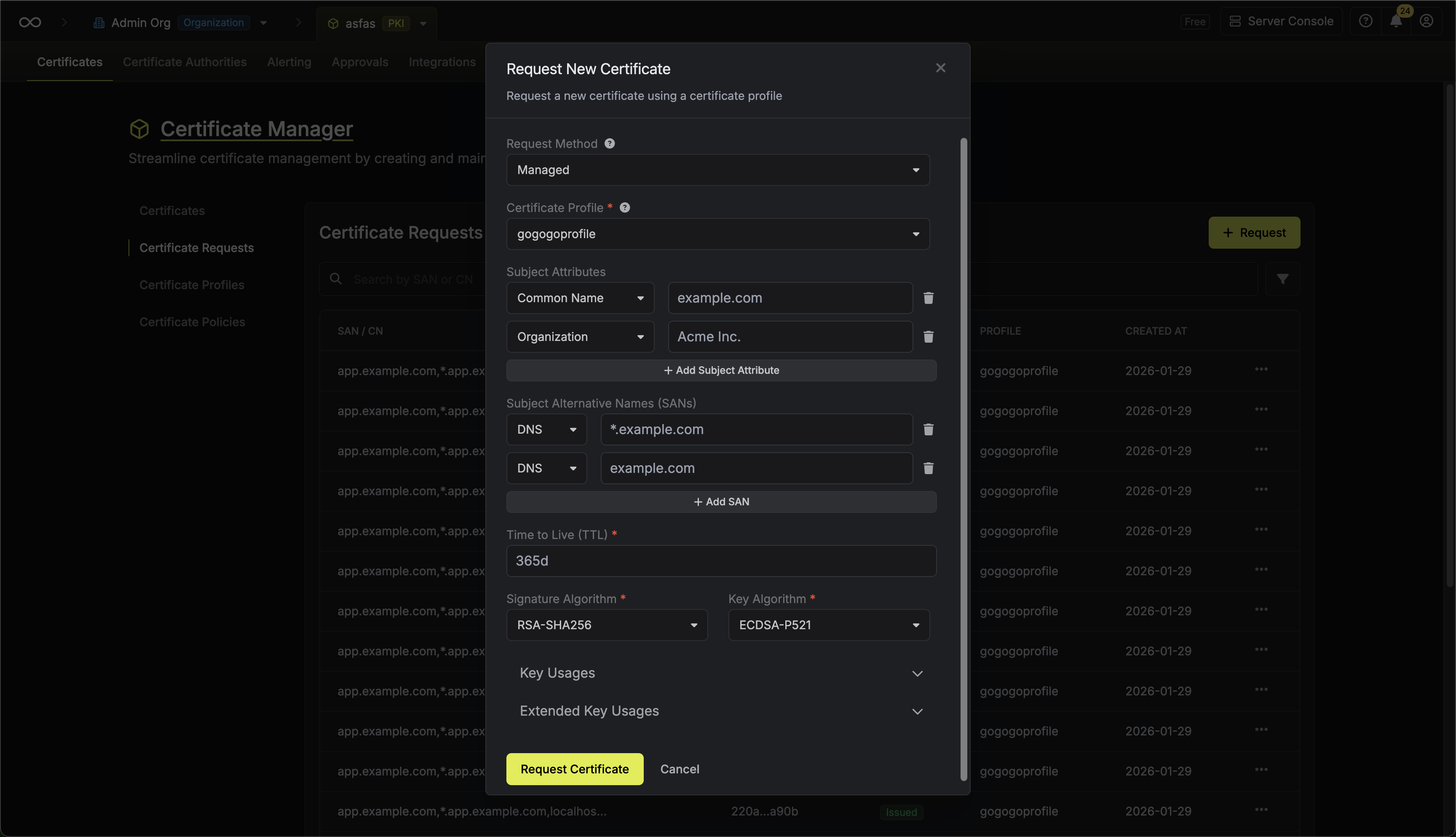 Paste your PEM-encoded CSR into the text area and specify the TTL for the certificate.
Paste your PEM-encoded CSR into the text area and specify the TTL for the certificate.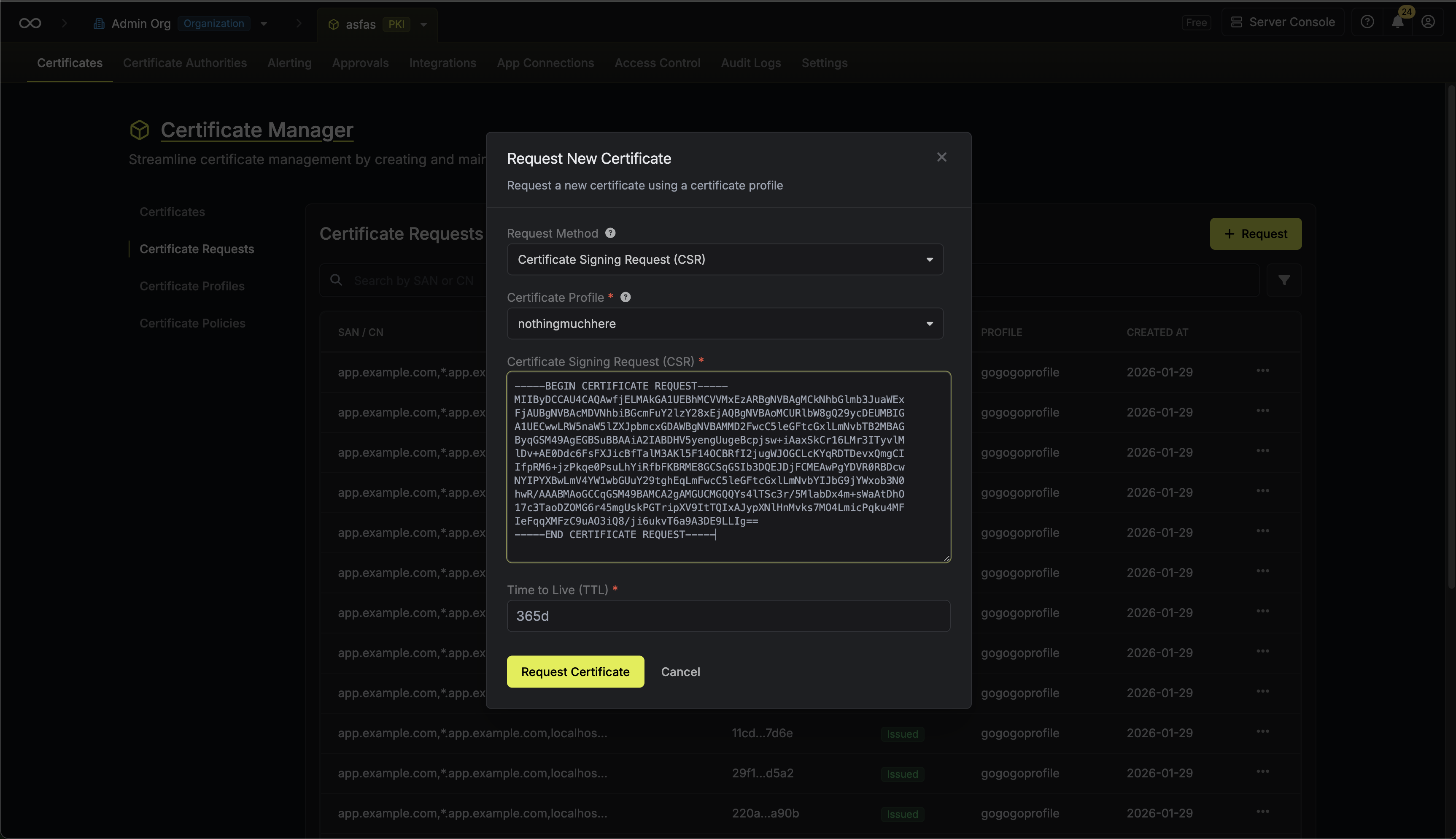
 Select CSR (Certificate Signing Request) as the Request Method, then choose your certificate profile.
Select CSR (Certificate Signing Request) as the Request Method, then choose your certificate profile. Paste your PEM-encoded CSR into the text area and specify the TTL for the certificate.
Paste your PEM-encoded CSR into the text area and specify the TTL for the certificate.
When using a CSR, the subject attributes, subject alternative names, and key algorithm are extracted from your CSR. You only need to specify the TTL for the certificate.
FAQ
When should I use Managed vs CSR?
When should I use Managed vs CSR?
Use Managed (recommended for most cases) when:
- You want Infisical to handle key generation and storage
- You need server-side auto-renewal capabilities
- You’re deploying certificates via certificate syncs to cloud providers
- You want the simplest setup with minimal configuration
- You don’t have specific requirements for key custody
- Your security policy requires private keys to be generated on the target system
- You’re using a Hardware Security Module (HSM) that generates and stores keys
- You need to reuse an existing private key
- You have compliance requirements that mandate key generation in a specific location
- You’re integrating with systems that generate their own CSRs (e.g., load balancers, appliances)
Certificates issued via CSR are not eligible for server-side auto-renewal since Infisical doesn’t have access to the private key. You’ll need to handle renewal by generating a new CSR and requesting a new certificate.
How do I renew a certificate issued via CSR?
How do I renew a certificate issued via CSR?
Certificates issued via CSR cannot be automatically renewed by Infisical since the private key is managed externally. To renew:
- Generate a new CSR using your existing private key (or generate a new key pair if desired)
- Request a new certificate using the new CSR
- Deploy the new certificate before the old one expires
Why am I getting a CSR format error in the UI?
Why am I getting a CSR format error in the UI?
Error: “CSR cannot be empty” or invalid format errorSolution: Ensure your CSR:
- Starts with
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE REQUEST----- - Ends with
-----END CERTIFICATE REQUEST----- - Contains valid base64-encoded content
Why am I getting a CSR format error via API?
Why am I getting a CSR format error via API?
Solution: When sending CSR via API JSON:
- Replace actual newlines with
\nin the JSON string - Include full PEM headers and footers
- Ensure proper JSON escaping
Why is my CSR failing policy validation?
Why is my CSR failing policy validation?
Policy validation errors occur when your CSR doesn’t comply with the certificate policy attached to the profile. Common errors include:
- Subject attributes: “Missing required attribute” or ” value does not match allowed patterns”
- Subject Alternative Names: ” SAN is not allowed by template policy” or “Required SAN not found”
- Key algorithm: “Key algorithm is not allowed by template policy”
- Signature algorithm: “Signature algorithm is not allowed by template policy”
- Review your certificate policy configuration in Project > Certificates > Certificate Policies
- Ensure your CSR includes all required attributes and SANs
- Ensure values match allowed patterns configured in the policy
- Verify your key algorithm is in the policy’s allowed list (common options: RSA_2048, RSA_4096, ECDSA_P256, ECDSA_P384)
Why can't I use CSR with self-signed certificates?
Why can't I use CSR with self-signed certificates?
Error: “Self-signed certificates are not supported for CSR signing”Solution: CSR-based issuance requires a Certificate Authority to sign the certificate.

