Concept
In order to ensure that your certificates are always up-to-date and not expired, you can set up alerting in Infisical for expiring CA and leaf certificates based on customizable filters.Guide to Creating an Alert
To create an alert, head to your Certificate Management Project > Alerting and press Create Certificate Alert.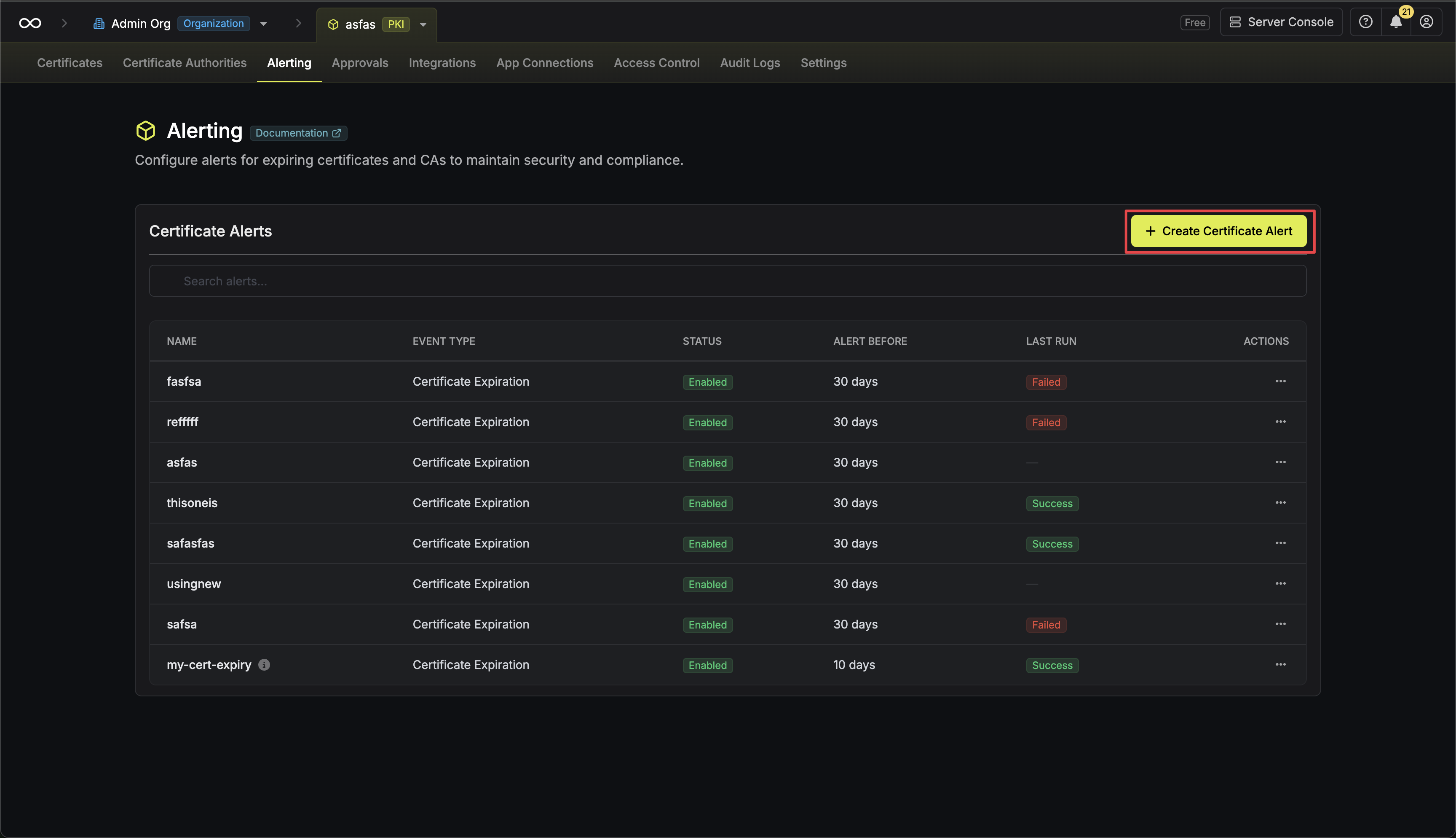
Field Descriptions
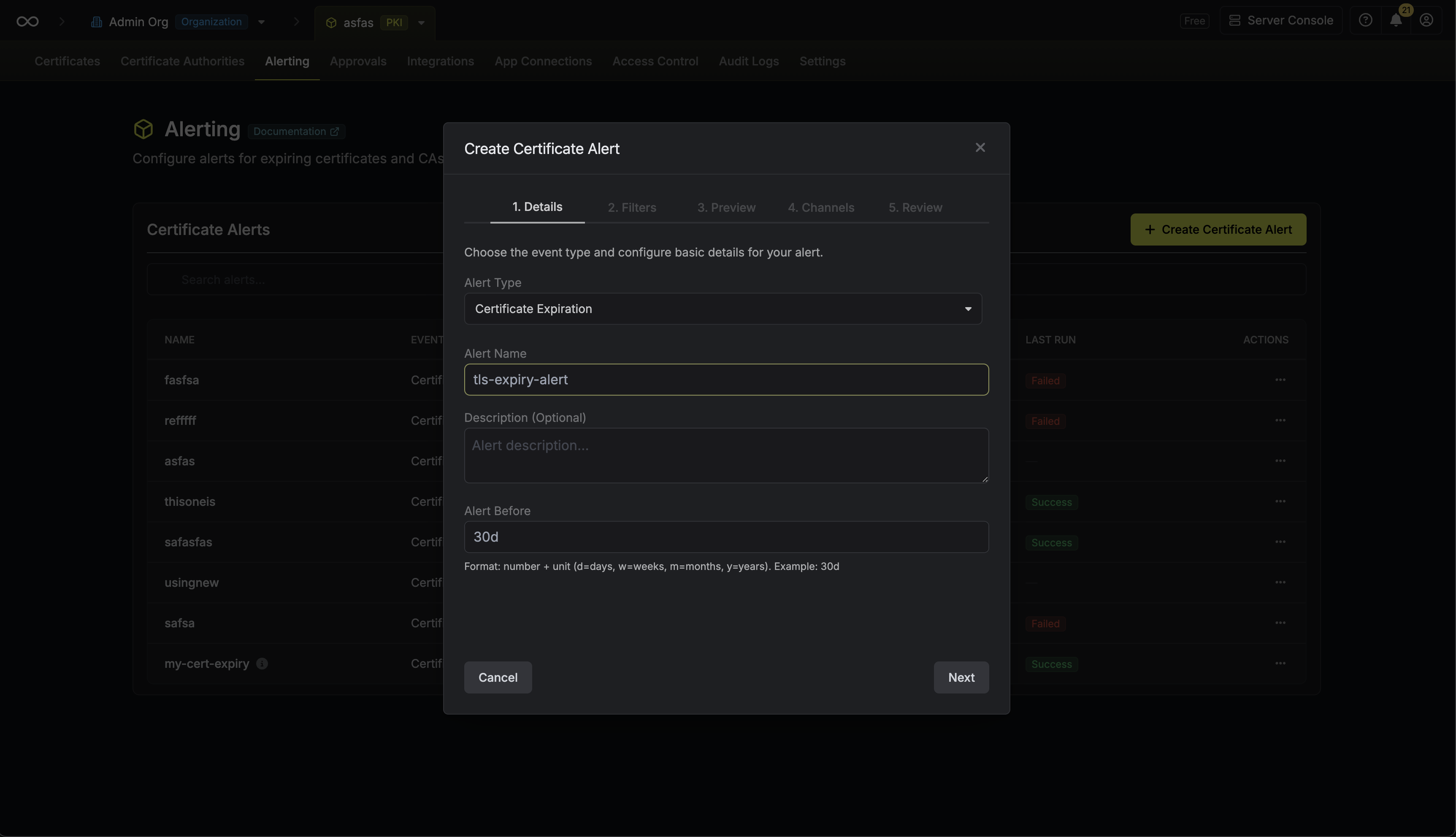
Here’s some guidance for each field in the alert configuration sequence:- Alert Type: The type of alert to create such as Certificate Expiration.
- Alert Name: A slug-friendly name for the alert such as
tls-expiry-alert. - Description: An optional description for the alert.
- Alert Before: The time before certificate expiration to trigger the alert such as 30 days denoted by
30d. - Filters: A list of filters that determine which certificates the alert applies to. Each row includes a Field, Operator, and Value to match against. For example, you can filter for certificates with a common name containing
example.comby setting the field to Common Name, the operator to Contains, and the value toexample.com.
Notification Channels
Alerts can be delivered through one or more notification channels:- Email: Send alert notifications to a list of email recipients. Enter one or more email addresses to notify when the alert triggers.
- Webhook: Send alert notifications to a webhook URL. The URL must use HTTPS. Optionally configure a signing secret to verify the authenticity of webhook payloads.
- Slack: Send alert notifications to a Slack channel via an Incoming Webhook. See detailed setup steps.
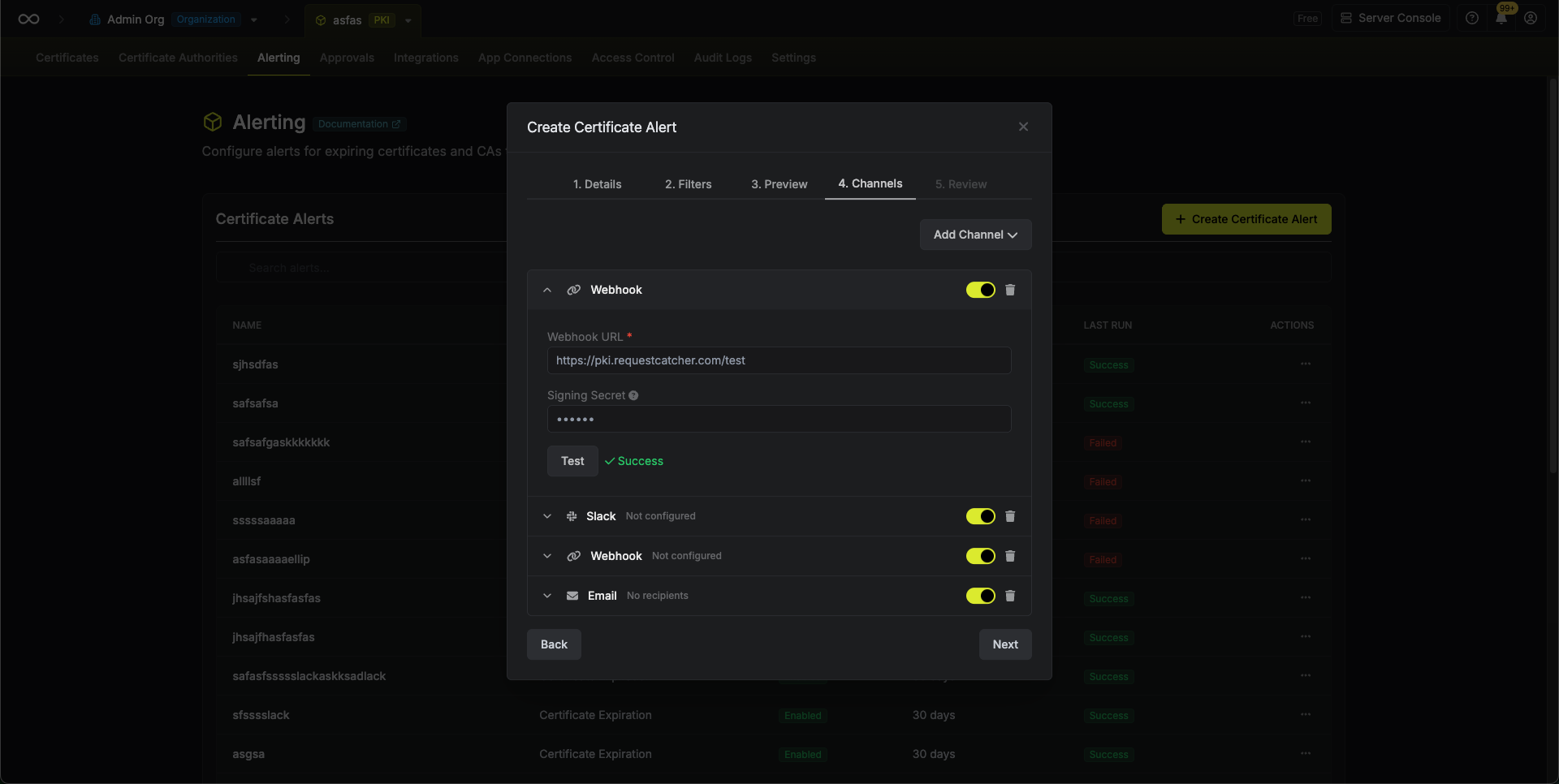
All configured channels must successfully deliver for an alert to be marked as complete. If any channel fails, the alert will retry until all channels succeed. Make sure all channels are working correctly to avoid repeated notifications.
Webhook Payload Format
Webhook notifications are sent as HTTP POST requests with a CloudEvents-compliant JSON payload.Webhook Signature Verification
If you configure a signing secret for your webhook channel, Infisical will include anx-infisical-signature header with each request. This allows you to verify that the webhook payload originated from Infisical.
The header format is:
<timestamp>is the Unix timestamp (in milliseconds) when the signature was generatedv1indicates the signature version<signature>is the HMAC-SHA256 signature of the payload
- Extract the timestamp and signature from the header
- Construct the signature payload by concatenating the timestamp, a period (
.), and the raw request body:{timestamp}.{body} - Compute an HMAC-SHA256 hash using your signing secret
- Compare the computed signature with the signature from the header
Slack Notifications
PKI alerts can be sent to Slack channels using Incoming Webhooks. Follow these steps to set up Slack notifications:Create a Slack App
- Go to the Slack API Apps page and click Create New App
- Select From scratch
- Give your app a name (e.g., “Infisical PKI Alerts”) and select the Slack workspace where you want to receive notifications
-
Click Create App
Enable Incoming Webhooks
- In your app settings, navigate to Incoming Webhooks in the left sidebar under “Features”
- Toggle Activate Incoming Webhooks to On
- Click Add New Webhook at the bottom of the page
- Select the channel where you want to receive alerts and click Allow
-
Copy the generated Webhook URL (it will look like
https://hooks.slack.com/services/T00000000/B00000000/XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX)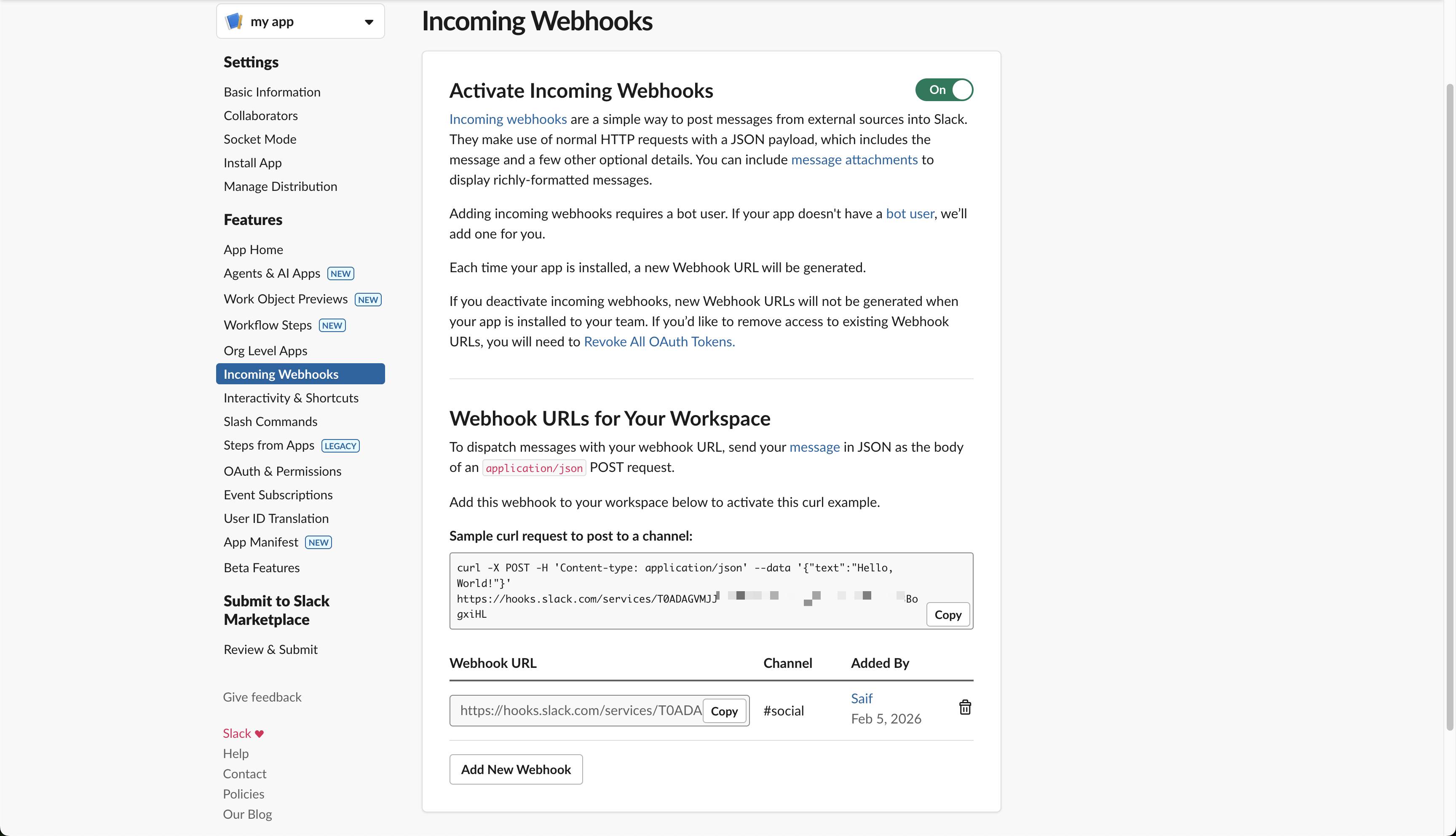
Keep your webhook URL secure. Anyone with access to it can post messages to your Slack channel.